Osgood-Schlatter Disease
- Bomi
- Jan 25, 2022
- 2 min read
Updated: Jan 30, 2022

Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Osgood-Schlatter Disease, also known as osteochondrosis, tibial tubercle apophysitis, or traction apophysitis of the tibial tubercle, causes anterior knee pain and swelling beneath the patella. It is mostly found in growing children who actively participate in sports that involve running and jumping.
*Patella, or kneecap, is a bone in front of the knee joint.
IMG Credit: James Heilman via Wikimedia Commons
Causes
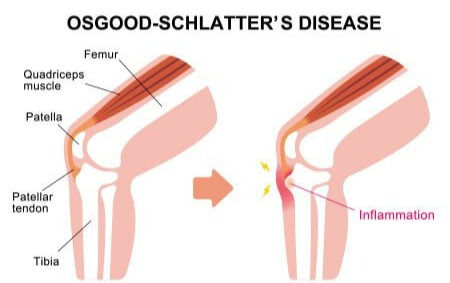
The growth spurt of children or adolescents and sports involving running, jumping, and swift changes of direction, such as basketball, volleyball, sprinting, gymnastics, and football, cause Osgood-Schlatter Disease. When the bones are still growing, areas around the growth plate are soft cartilage, not mature bone. The quadriceps are connected
IMG Credit: Yashoda Hospitals
to patella and patellar tendon is attached to the growth plate in the tibia. As the quadriceps pull the patella, the patella tendon gets tension and pulls the tibia where the growth plate is located. Repetitive movement of legs could hurt tissues around the growth plate and swell them up.
*Tibia, or shinbone, is a long bone in the lower leg that connects the knee and ankle.
Quadriceps are a group of four muscles located in the front thigh. They are the largest and strongest muscles in the body.

Symptoms
The indicatives of Osgood-Schlatter Disease are knee pain and swelling beneath the patella. The patient usually experiences the condition on one knee, but rarely in both knees. Kneeling and intense sports can be painful. Even after the symptoms resolve with the closure of the growth plate, a bump under the patella could remain. However, it does not affect knee function.
IMG Credit: Cureu
Treatment
There is no special treatment for Osgood-Schlatter Disease. Taking rest between activities and avoiding intense exercise are needed. Knee pain can be relieved using ice packs and NSAIDs. The pain usually goes away when a patient become skeletally mature. Nevertheless, surgery is needed in some rare cases. If bone fragments are left in the patellar tendon when the bone was replacing cartilage, they can cause tendon irritation. Those bone fragments should be removed through surgery in order to fully relieve the pain.
*NSAID stands for Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and they are commonly used to reduce pain, inflammation, and lower fever.
Reference
NHS Choices, NHS, www.nhs.uk/conditions/nsaids/.
“Broken Tibia-Fibula (Shinbone/Calf Bone): Boston Children's Hospital.” Boston Childrens Hospital, www.childrenshospital.org/conditions-and-treatments/conditions/b/broken-tibia-fibula-shin-bone-calf.
Linderbaum, Kendra. “Osgood-Schlatter Disease Surgery for Adults & What to Expect After.” BraceAbility, BraceAbility, 25 May 2018, www.braceability.com/blogs/articles/osgood-schlatters-surgery.
“Osgood-Schlatter Disease.” Johns Hopkins Medicine, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/osgoodschlatter-disease.
“Osgood-Schlatter Disease.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 9 Oct. 2019, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osgood-schlatter-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354864.
“Patellar Fractures (Broken Kneecap) - OrthoInfo - AAOS.” OrthoInfo, orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/patellar-kneecap-fractures/.
Person. “Quadriceps Anatomy, Muscle Function, Injuries, Exercises, and More.” Healthline, Healthline Media, 16 June 2020, www.healthline.com/health/quadriceps.
Smith, James M. “Osgood Schlatter Disease.” StatPearls [Internet]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 30 July 2021, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441995/.




Comments