Asthma
- Haeri
- Dec 25, 2022
- 2 min read
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease in which the bronchi are repeatedly narrowed by allergic inflammation, making it hard to breathe. Most asthma patients experience repeated symptoms of shortness of breath and chest tightness. Recently, the number of asthma patients is increasing worldwide.
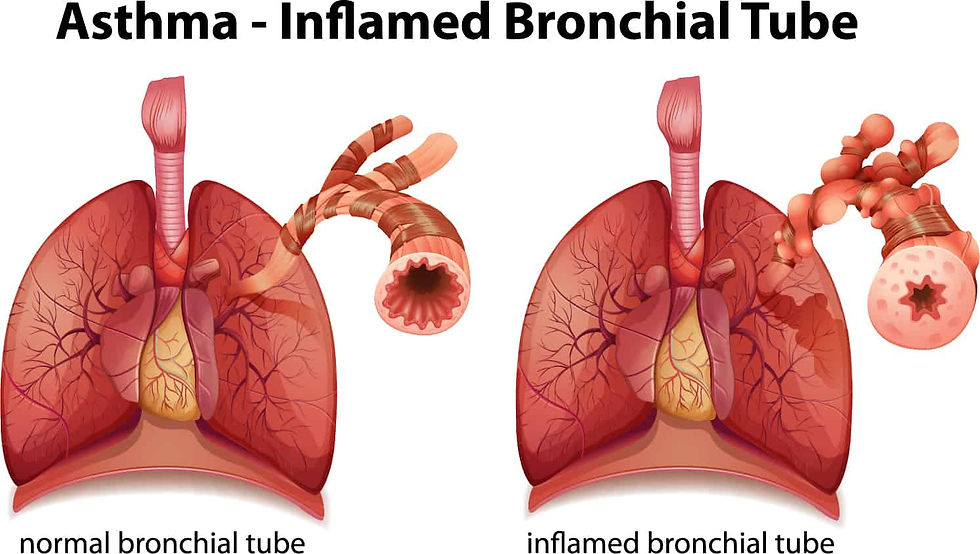
IMG Credit: asthma.ca
1. Causes
Although the specific causes of Asthma are unknown, it is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The chance of acquiring asthma is increased by a number of genes as well as by a family history of the condition. For environmental factors, allergens or triggering substances in the air are the main cause. Each person's individual triggering substance for an asthma attack is different, but the common ones include air pollution, pollen, dust, animals, mold, and certain medications.
2. Symptoms
Asthma patients' symptoms change frequently, are complex, and vary from patient to patient, so they cannot be identified as one. However, characteristic symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and dyspnea. Wheezing refers to a whistling sound similar to a whistle when inhaling and exhaling, and the cough of asthmatic patients is paroxysmal and appears worse at night. Dyspnea is also a common symptom, which means difficulty breathing. These symptoms occur when an asthma attack happens. Asthma attacks cause the airways in the lungs to swell, itch, and become mucus-filled, which makes it difficult to breathe.
3. Treatment
Even though there is no known cure for asthma, there are treatments and medications that can control the symptoms and prevent an asthma attack from happening. The first step is to manage the environment. A person with asthma should first avoid or reduce contact with triggering substances by vacuuming, removing dust, and altering the surroundings. There are also medications that can be used to treat asthma. The medications are largely divided into long-term disease control medicines and short-acting symptom relievers. Long-term disease controllers inhibit the inflammatory response of the airways in the long term and prevent asthma attacks. This medicine is used regularly every day, even when symptoms are not present. Short-acting symptom relievers are medicines that relieve symptoms immediately by dilating the bronchi. It is used only when symptoms are severe or when an asthma attack has occurred and is mostly in the form of an inhaler. In addition to this, there is one more treatment, however, this requires long-term treatment of at least 3 years. This is immunotherapy, which is a treatment that suppresses hypersensitivity to allergens. This treatment is long-lasting and prevents attacks even when exposed to the triggering substances. However, the effect can be seen only in patients with a clear allergen, and as mentioned before, at least 3 years of treatment is required.
Reference




Comments